Melasma (Chloasma) Overview
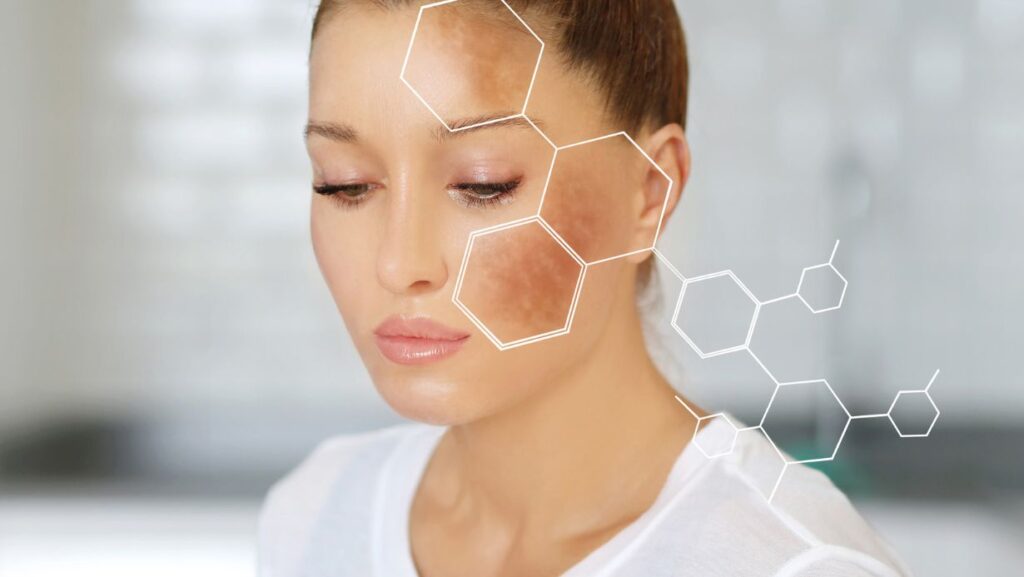
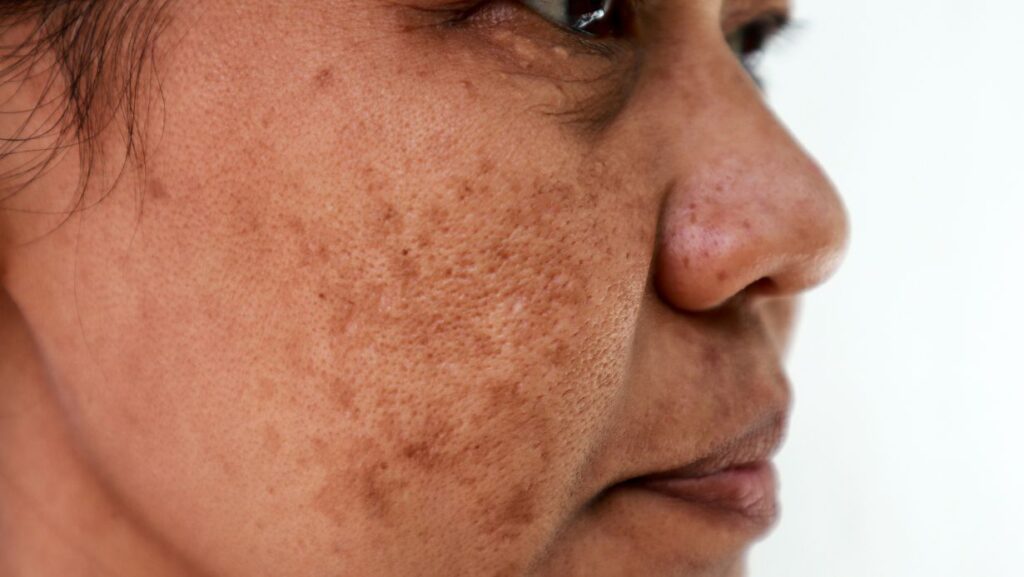
Melasma is a skin condition characterised by dark patches of pigment on the face, neck, arms or upper body.
It is more common in women, particularly in pregnancy (known as a pregnancy mask) and in people with darker skin who expose their skin to the sun regularly. The condition is also called chloasma.
The pigmented areas are noticeably darker than the surrounding skin but are not different in texture, are usually smooth and are not itchy or painful. In most sufferers, the dark pigmentation becomes more noticeable in the summer and may even disappear in the winter. It seems to be light induced and is not caused by an infection, so is not contagious. It is not thought to be an allergic reaction to light and is not cancerous. However, as the dark patches are visible in everyday life they can be a cosmetic concern.
The contributing factors for melasma are: pregnancy; hormonal treatments such as oral contraceptives; medical conditions that affect hormone levels such as the menopause; exposure to sunshine or sun-beds. These factors are known to be linked to melasma occurrence and can exacerbate the condition once it is present.
The best way to alleviate melasma is to avoid the known trigger factors. During pregnancy, avoid exposure to the sun and sunbeds, the condition usually dissipates once hormone levels reduce after birth. Other sufferers should also avoid open exposure to the sun whenever possible, and use sun blocking products with a very high sun protection factor, at least SPF 50, every day.
There are skin treatments that can be used to make melasma less visible and improve the appearance of the skin.
Skin lightening creams are also helpful, they contain chemicals that interfere with the pigment forming cells and reduce synthesis of the pigment. Hydroquinone is a common active ingredient, other creams may contain azelaic acid or retinoid, both of which are often used to treat acne but can also improve the appearance of melasma. These creams can sometimes irritate the skin so should be recommended and prescribed by a doctor or nurse prescriber.
The most important thing for someone with melasma is to avoid the sun and never use a sunbed. The good news is, once the right treatment has been found sustained sun protection should avoid any further pigmentation problems.
Melasma (Chloasma) Treatments
-
- XEO Laser skin resurfacing £90
- Fractional Laser £150
- Specialist Skin Creams From £90